In the ever-evolving world of marketing, understanding the effectiveness of different strategies and channels is crucial for business owners and marketing professionals alike. One key aspect of this understanding is attribution modeling, which allows us to determine the impact of each touchpoint in a customer’s journey. One popular attribution model being used today is the Linear Attribution Model.
In this blog post, we will delve into the concept of the Linear Attribution Model, its benefits, and how it can be leveraged to optimize marketing efforts.
What is the Linear Attribution Model in Marketing?
The Linear Attribution Model is a method used to assign equal credit to every touchpoint that a customer interacts with during their journey. Unlike other traditional models, such as Last-Click or First-Click, which give all credit to the final or initial touchpoint, the Linear Attribution Model acknowledges the importance of each interaction.
This model recognizes that customers are influenced by various marketing channels at different stages, and no single touchpoint should receive all the credit. Instead, equal weightage is assigned to every touchpoint, allowing businesses to have a more holistic view of their marketing efforts.
Benefits of the Linear Attribution Model for Marketing
Implementing the Linear Attribution Model offers several benefits for businesses:
Enhanced Insights
By using the Linear Attribution Model, businesses gain valuable insights into the entire customer journey. Instead of solely focusing on the last or first touchpoint, companies can analyze the cumulative impact of all touchpoints in driving conversions. This comprehensive view provides a deeper understanding of the customer’s decision-making process and allows for more informed marketing strategies.
Improved Budget Allocation
With the Linear Attribution Model, businesses can allocate their marketing budget more effectively. By recognizing the contribution of each touchpoint, companies can invest resources in optimizing all channels rather than concentrating solely on the last-click conversion. This balanced approach ensures a well-rounded marketing strategy, leading to improved results and ROI.
Better Campaign Optimization
The Linear Attribution Model enables marketers to identify the strengths and weaknesses of each touchpoint. By analyzing the performance of various channels across the customer journey, businesses can optimize their campaigns accordingly. This data-driven approach helps to refine marketing efforts, improve targeting, and enhance overall campaign performance.
Other Marketing Attribution Models
Many different marketing attribution models exist, each presenting a distinct perspective on how to distribute credit. Here are the other most common types of marketing attribution models:
- Last-Touch Attribution: Contrary to first-touch attribution, last-touch attribution attributes all credit for a conversion or sale to the final touchpoint before the customer converts. This method gives the most credit to the last marketing activity the customer engaged with, like clicking on a specific ad or link that leads to the purchase. While it may be straightforward, last-touch attribution overlooks the cumulative impact of previous touchpoints that may have nurtured the lead.
- First-Touch Attribution: First-touch attribution assigns full credit for a conversion or sale to the very first interaction a customer has with the business.
- Time Decay Attribution: This model assigns more credit to touchpoints closer to the time of conversion. The touchpoints that are closer in time receive a higher proportion of the credit.
Even More Attribution Models
- Position-Based (U-Shaped) Attribution: Also known as U-Shaped attribution, this model gives a larger portion of the credit to the first and last touchpoints, while the remaining credit is distributed among the touchpoints in between. This recognizes the importance of both the initial awareness and the final decision-making touchpoints.
- Algorithmic Attribution: Algorithmic attribution models use complex algorithms and machine learning to assign credit based on the observed patterns in historical data. They take into account multiple touchpoints, their order, and various factors to determine the optimal credit distribution.
- Custom Attribution: Businesses can create their own attribution models tailored to their specific needs and goals. This might involve combining elements of different models or incorporating additional factors that are unique to the business.
- Data-Driven Attribution: This model uses statistical analysis to analyze the historical performance of different touchpoints and assigns credit based on their actual impact on conversions.
- Multi-Touch Attribution: Multi-touch attribution considers multiple touchpoints throughout the customer journey and attributes credit to all relevant touchpoints that contributed to the conversion.
- Closed-Loop Attribution: tracks the entire customer journey, from initial touchpoints to the final conversion or purchase, and allows marketers to understand precisely which marketing activities contribute most significantly to revenue generation.
Closed Loop vs. Linear Attribution
Closed Loop attribution tracks the entire customer journey and uses advanced tracking capabilities to understand which exact marketing activities contributed to a conversion or sale.
On the other hand, linear attribution is a simpler attribution model in which it credits every trackable step of a customer’s journey to a sale/conversion equally.
How to Leverage the Linear Attribution Model
To successfully leverage the Linear Attribution Model, businesses can follow these steps:
Data Collection and Integration
The first step is to ensure accurate and comprehensive data collection from multiple marketing channels. Integrating data sources into a unified system allows for better analysis and insights. Implementing tools like Google Analytics or marketing automation platforms can simplify this process.
Defining Touchpoints
Identify and define the touchpoints along the customer journey. These touchpoints may include organic search, Google Ads, social media ads, email marketing, influencer partnerships, and more. Each touchpoint should be tracked and measured to evaluate its impact on conversions.
Weighting and Analysis
Assign equal weightage to each touchpoint in the attribution model. Analyze the data collected to understand how these touchpoints contribute to conversion rates, customer engagement, and overall revenue. Use this information to adjust and optimize marketing strategies accordingly.
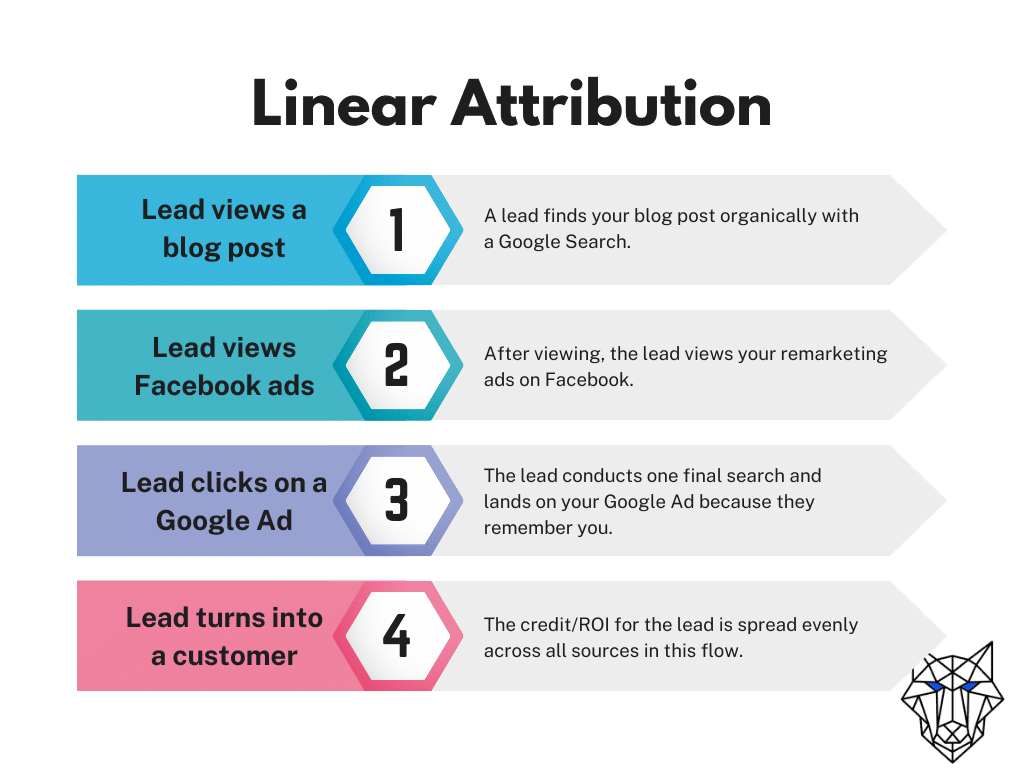
To illustrate, if a user visits your blog post from a search query about an issue, receives remarketing advertisements on social media afterward, later performs additional searches about services to solve their problem, and then clicks on your Google Ad, each step should get equal credit for converting the sale.
As a business, you can split the return on ad spend evenly across all channels.
Continuous Testing and Refinement
Marketing is an iterative process, and the Linear Attribution Model is no exception. Continuously test, measure, and refine your attribution model to adapt to evolving customer behavior and market trends. This ongoing optimization ensures that your marketing efforts remain effective and relevant.
Conclusion
The Linear Attribution Model provides a fair and comprehensive way to evaluate the impact of different touchpoints throughout the customer journey. By assigning equal credit to each interaction, businesses gain enhanced insights, improve budget allocation, and optimize their campaigns more effectively.
Leveraging this model, along with data collection, defining touchpoints, weighting, and analysis, as well as continuous testing and refinement, businesses can unlock the true potential of their marketing efforts and drive better results.
Ready to take your marketing to the next level? Get a digital marketing proposal today.





